Table of Contents
CNC, Computer Numerical Control, means inputting precise commands, translate and calculate via computer, and transmitting the information to the driver and motor through the positioning control system. It is widely used in digital dentistry because its product consistency compared to 3D printing and its exclusivity in ceramic output.
Two years ago, the world’s major CNC manufacturers joined the digital dental field, and all sorts of milling machines emerged. Now, only a few manufacturers still exist, and they have established alliances with other upstream and downstream manufacturers. These manufacturers have been focused on dental CNC since the beginning, and strive to adjust the complicated industrial instruments into machines that dentist or dental technician without industrial background can operate, unlike the other manufactures in the CNC industry. This shows that focusing on the targeted customer and paying attention to customer needs is the key to survival in the market.
These manufacturers are: Dentsply Sirona , Planmeca , Ivoclar Digital , imes-icore , vhf , DGSHAPE (Roland) , and IDC (Amann Girrbach).
Each manufacturer also introduces different milling machines for different users’ required production quantity and material requirements, ranging from huge lab machines with automatic storage tray, automatic wet/dry switching cleaning tank to quiet and efficient chairside milling machines. I personally believe that only chair-side milling machines can fully unleash the potential of digital dentistry. Moreover, the simpler the more difficult it is. Minimizing huge milling machines for chairside use challenges the hardware capability of the manufacturer. Therefore, the main purpose of this article is to review the mainstream chairside milling machines in the market in 2019.
The evaluation checklist of milling machines
1. How many axes: affects clinical indications
Currently, the milling machine on the market can be roughly divided into two categories, four-axis (XYZA) and five-axis (XYZAB) . The biggest difference between the two is the size of the area that cannot be milled. The area that cannot be milled in four-axis machines is shown in Figure 1. Theoretically, there shouldn’t be places that a five-axis cannot mill. However, due to the path of the bur and the ceramic block mounting area, there are still some parts that cannot be milled (Fig. 2), but the area is relatively small and less susceptible to undercuts. This limitation also directly leads to different clinical indications. Most restorations shouldn’t have undercuts due to the need for path of insertion, so the only contraindication of four-axis miller is long span implant bridge and surgical guide for multiple implants. However, both of these are usually not included in chair-side treatment cases, so most chair-side millers are four-axis machines.
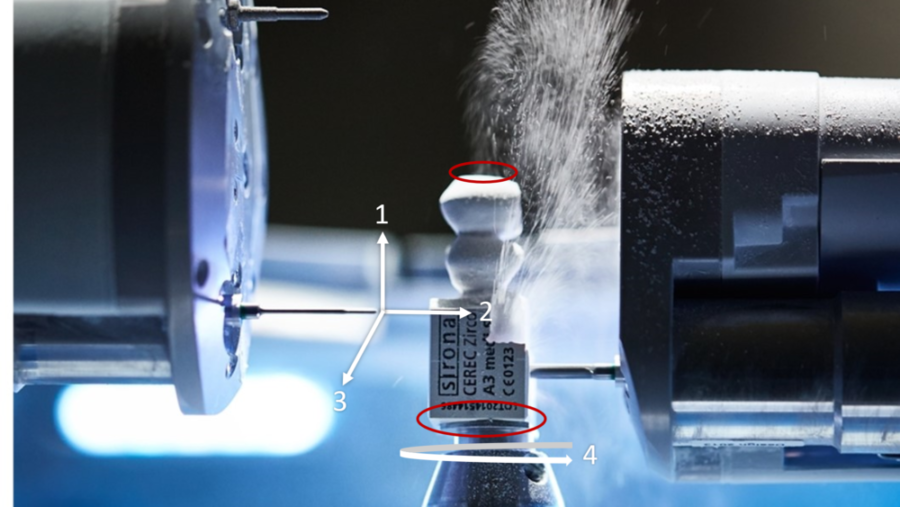
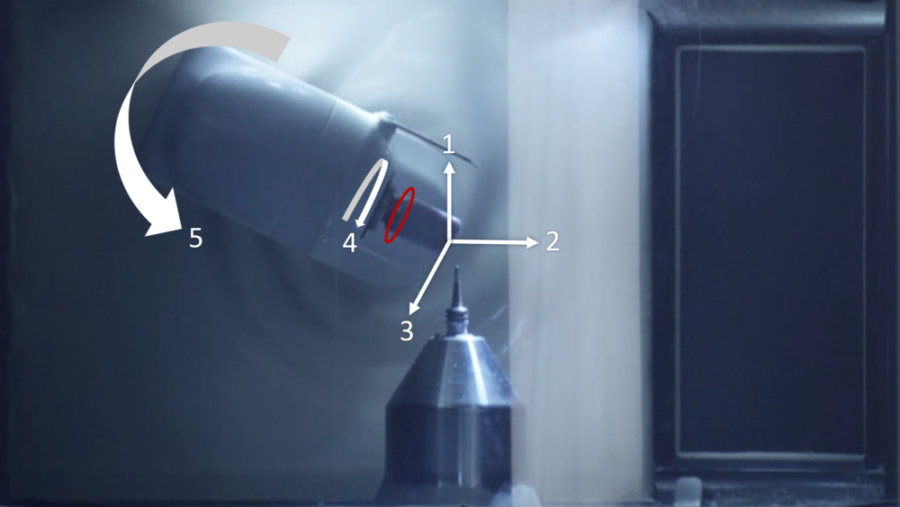
2. The size of the smallest bur: affects marginal integrity and preparation requirements
In theory, the smaller the bur is, the better the resolution will be, and the less over-milling will occur during milling. But unfortunately, smaller burs are more fragile. Even if the smaller burs do not break, the bending of the bur when under stress will introduce errors. Therefore, the smallest bur size that can be achieved without excessively weakening its own strength is the resolution of the miller, which affects the marginal integrity that dentists care so much about and is also effected by the roundness of the preparation. Currently, 0.5 – 0.6 mm is the limit of most milling machines. Few of the manufacturers can use 0.3mm round burs during the milling of zirconia.
3. Applicable block type: affects clinical indications
Basically, most chair-side millers can mill all kinds of glass ceramics, zirconia, and resin blocks. The biggest difference is that some millers can also mill sintered metal used for customized implant abutments.
4. Maximum ceramic block size: affects size limitation of product
Most chair-side milling machines mill blocks and not disks. Larger blocks are usually in PMMA , e.max , and zirconia, which are used for bridge prosthesis or surgical guide. Because of its shrinkage during sintering, zirconia blocks tend to be bigger. Therefore, the size of the block that can be placed in the miller limits the size of the prosthesis that can be fabricated.
5. Maximum scheduled milling amount: affects the automated productivity
Due to the large output quantity requirement of lab millers, overnight milling or automated milling is needed. Therefore, the amount that can be scheduled and change blocks automatically greatly affects productivity and variety. Although most chair-side millers have short milling time (single restoration or same-day delivery cases) and do not require this function, some machines still have scheduling capabilities.
6. Single crown milling time: affects digital workflow efficiency and total output
The speed of milling a single crown in chair-side CAD/CAM is very important. For only one crown, the difference between ten minutes and twenty minutes doesn’t seem much, but when you have four or five restorations milling at the same time, the difference between fifty minutes and one hundred minutes makes a big difference. Especially when multiple dentists are performing digital treatment at the same time, the time wasted waiting for the machine to mill and difficulty to arrange appointments deliver or even working over-time adds intangible costs.
7. Dry and wet milling function: affects zirconia sintering time
When zirconia is sintered, it needs to start from a dry state. If it is wet, an additional 30 minutes of pre-dry drying process is required. Because of this, manufacturers also introduce dry milling, or models that can switch between wet and dry milling. However, according to the experience of most dental workers, most dry/wet combined machines are still often fixed in a single mode. The main reason is that if the residual zirconia powder is not cleaned thoroughly during dry and wet switching, it will flow into pipelines of the machine with water and cause damage to the miller, and currently only a few lab millers have automatic switching tank cleaning function.
8. Air compressor, external water tank: affects noise and space
The milling machine is powered by air pressure, so early models usually had to be connected to a source of high-pressure air, either from a central control room or an external air compressor. However, placing external air compressors in the clinic causes excessive noise and space occupation. Therefore, the air compressor is usually integrated into the chair-side milling machine nowadays. Since the milling subject is relatively simple and small, the amount of pressured air needed is also relatively small. The water used in the milling machine is usually recycled. As the powder produced during milling is mixed into the water, the water will get dirty eventually and needs to be changed. Therefore, due to the large output of lab milling machine, most are equipped with an external large-capacity water tank, while the chair-side milling machines usually use smaller internal water tanks.
9. Software operation mode: affects the user’s learning curve, debugging ability
The drive and milling strategy of the miller requires software control. There are also many parameters in the software for the adjustment of milling. In the past, some millers need to be connected to a laptop when milling. Nowadays, in addition to highly integrated systems (such as CEREC, Planmeca) that integrate CAD with CAM software, some new chair-side models also have built-in computer with touch interface, simplifying the parameters and input process for dentists and technicians.
10. Special milling strategy: affects milling efficiency, detail integrity, material limitations
As the requirement for clinical efficiency is increased for different restorative types, many manufacturers have continued to improve their milling strategy, which includes: milling path, bur selection, moving speed, contact angle, torque… etc. There are a few modes that are often mentioned.
Carving mode: cutting away large portions of material that will not be used at the beginning of milling, greatly reducing traveling path of the bur and saving time
Thrilling mode: Drilling vertical holes for implant restorations, so that ceramic blocks without built-in holes can also be connected to all sorts of implant abutments.
Margin protection: Marking the margin area that dentists care most about on the software, and uses the lightest force and finest bur to mill this area to prevent chipping.

(Source: https://www.amanngirrbach.com/en/products/production-cam/ceramill-mikro-ic/)

Price: affects your bank account numbers
Um … does this need explanation? The price mentioned in this article is the MSRP quoted at IDS 2019. The actual retail price may differ.
A brief review of milling machines in the market
Dentsply Sirona – MC XL

A four-axis miller announced by Sirona since 2007, inherits the simultaneous milling of left and right double-bur starting from CEREC 2 to increase efficiency. A second set of finer burs (EF Bur 0.6mm) was added. The burs do not need to be changed during the milling process. A rotating motor is used to utilize the second set of burs, reducing the time required for bur changing. The operating software of the miller has been integrated into the “CEREC” software package along with oral scanning and CAD. As the software is updated, stability, surface characteristics, marginal integrity and milling strategies are also updated. Also, because CAD software is integrated, it provides margin protection when milling, along with built-in bur check and foolproof function. Although it has been on the market for 12 years, it is still on par with the other new machines seen this year. It has shortest milling time for single crown in all the chair-side milling machines.
PLANMECA – Planmill 40 S

Planmeca (formerly E4D) introduced the Planmill 40 follow-up model in 2017. “S” is the abbreviation of SMART, meaning it can automatically calculate the optimal milling path, automatic cleaning and maintenance, automatically change damaged or broken burs, aiming to reduce the need of maintenance by engineers. Planmeca also offers a fully integrated workflow, the same double-bur design, with a single crown milling time of about 10 minutes. It uses exclusive porcelain block handles, but most of the current material suppliers offer handles for Planmeca, so that shouldn’t be a problem. It is the cheapest in this review. The biggest drawback is that the smallest bur diameter is 1mm, which is significantly bigger than other brands.

(Source: https://www.planmeca.com/software/news-videos/releases/releases-list/release-2-0-planmeca-plancam/ )
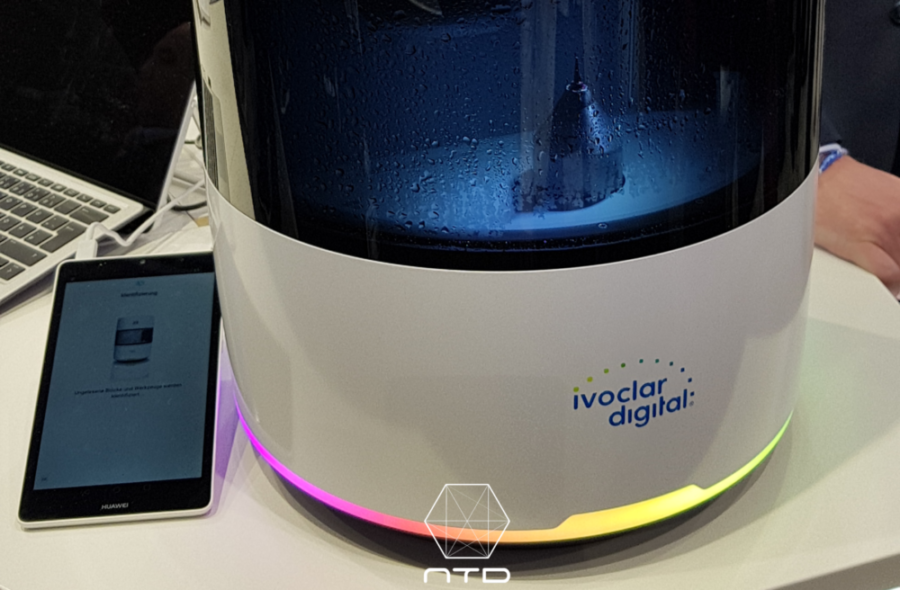
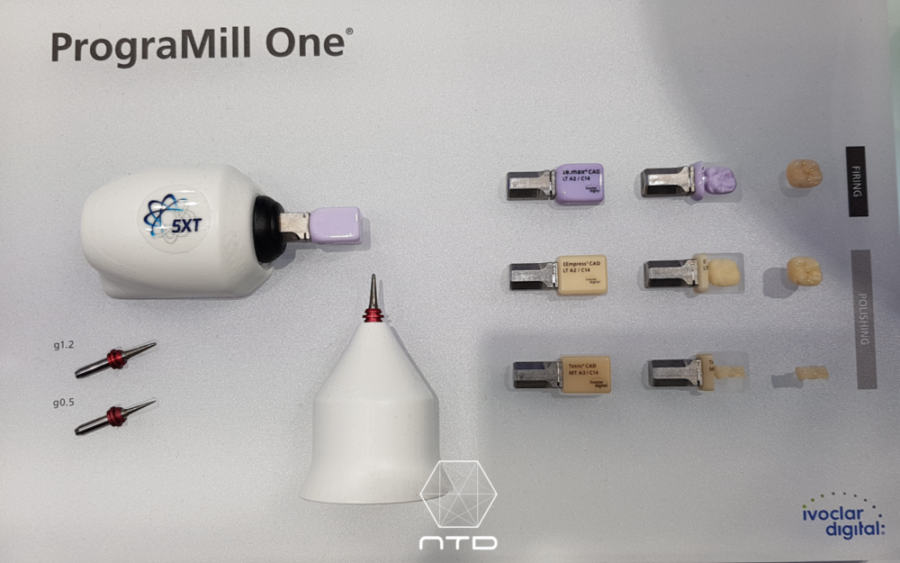
Ivoclar Digital – Programill One

Programill One is a part of Ivoclar Digital, the new product line announced in IDS 2017, and is the only “five-axis” chair-side milling machine on the market, with the capability of scheduling five blocks for auto-change. It is capable of being remote controlled by apps on tablets. Due to its minimalistic and beautiful design and five-axis milling capability, it caused a sensation when it was first announced. However, after a closer look, you will find that this machine can only use Ivoclar’s own porcelain blocks, which limits the choice. The bigger problem is its small space. Only restorations shorter than 45 mm can be milled. Longer bridge or guiding plate cannot be milled. I asked the manufacturer this year if this will be improved, but it seems that they have no such plan at the present.


imes-icore – CORiTEC One

The German milling machine manufacturer imes-icore launched their new four-axis model in IDS 2019 this year, which boasts wet and dry milling capability. It is targeted for chairside, but it is slightly larger, similar to a lab-use milling machine. It has a built-in air compressor and water tank. It can mill three porcelain blocks at the same time, and can also mill metal prefabricated abutments and PEEK of specific brands. I believe the biggest improvement is the integration of operating software and the user-friendly interface. The more intuitive operation makes it easier for the user. It is a milling machine with great clinical potential.

vhf – Z4

Vhf is a German heavy industry company specializing in grinding machines in various fields. The dental product positioning of the factory is quite clear. Z4 is defined as the machine used by Same-day dentistry . It is small in size, has built-in water tank and air pressure, and comes with software. The operation interface does not require an external computer, the software comes with a foolproof device, and the wrong drill pin will remind you. Using a standard ceramic block handle, it provides a 2 second quick-connect function, only single mill at a time, and can be ground to a pre-prefabricated abutments of titanium . It is basically positioned close to CORiTEC One on the market , but in smaller size.
DGSHAPE – DWX 42W

DGSHAPE is a subsidiary that was split by Roland in Japan in 2017. Since it saw the business opportunities of three-dimensional printing, the subsidiary was established to expand the original brand, from pure dental grinder business to 3D printing and medical use. Rapid prototyping. Therefore, this year DGSHAPE launched a new dental 3D printer, which was not significantly updated. The DWX-42W has a Curving mode and a special burr designed for this purpose to improve the grinding efficiency. It can grind three porcelain blocks at the same time. However, the disadvantage is that the internal air compressor is still needed because it is not completely positioned in the clinic. There is also an additional external control computer, no built-in control display, and fewer material options.

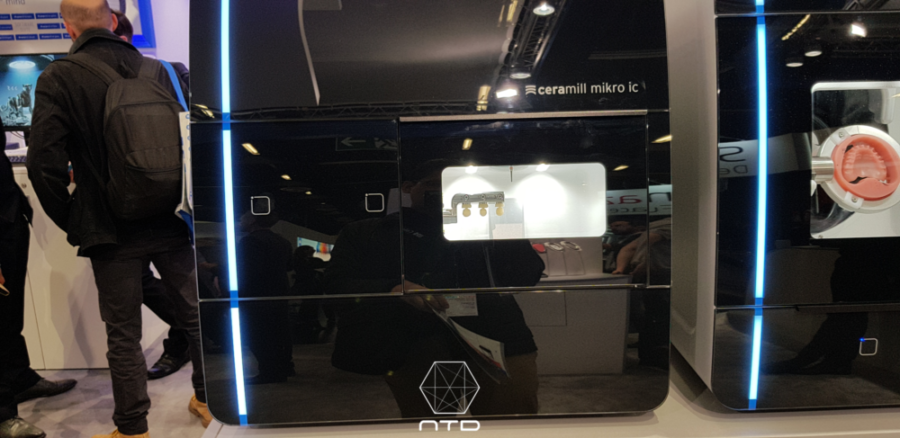
IDC – MIKRO IC

IDC is a sub-brand launched this year by Amann Girrbach, a hardcore German grinding machine articulator manufacturer , to create a complete Chair-side Digital Workflow . This machine is actually a Ceramill matik ic . The difference is that the original external water tank is hidden in the fuselage because of its chairside orientation, but the Amann Girrbach specialization of various grinding strategies (Curving mode , Thrilling mode, etc. ) is retained . It also has the smallest drill diameter of all models. This machine is currently labelled by major brands such as Straumann and Carestream , and is the favorite chairside grinder for the manufacturer to integrate the digital process.


Chairside CNC Specifications Comparison
Finally, the most important one, I attached the specification comparison table that I sorted out under the IDS 2019 exhibition. ( Because I was actually tired in the past few days, I also hope that everyone will help me a little. )
Sum up
According to this arrangement, you can use the characteristics of the grinder in each clinic to easily locate the market: If you are looking for a machine that is simple to operate, integrated and complete, and the most efficient grinding, CEREC MCXL will be your choice; If you have budgetary considerations, the Planmill 40 S is the most affordable model; if you work with many types of materials, CORiTEC One offers almost any choice of materials; if you want the highest detail, Or want to use the same grinder with major manufacturers, Amann Girrbach ‘s Mikro IC (PL900S) is the most popular machine; if you want the clinic to have a taste that looks fashionable, Programill One is definitely a light up in your clinic. High-level art; if you act steadily and low-profile, Z4 data performance is not up to the top but there are no obvious shortcomings.
Above, I hope that this article will help the practitioners who want to step into the Chair-side CAD/CAM in the era of digital dental, so that the most expensive and least informative piece of the grinding machine becomes clear.
– Adjunct Attending physician of Taipei Veterans General Hospital Prosthetic Dentistry Department
– Member of The Academy of Prosthetic Dentistry, ROC TAIWAN
– Specialist of Taiwan Academy of Digital Dentistry
– Lecturer at CEREC Asia Training Facility

Excelente article